Carbon farming in the European forestry sector
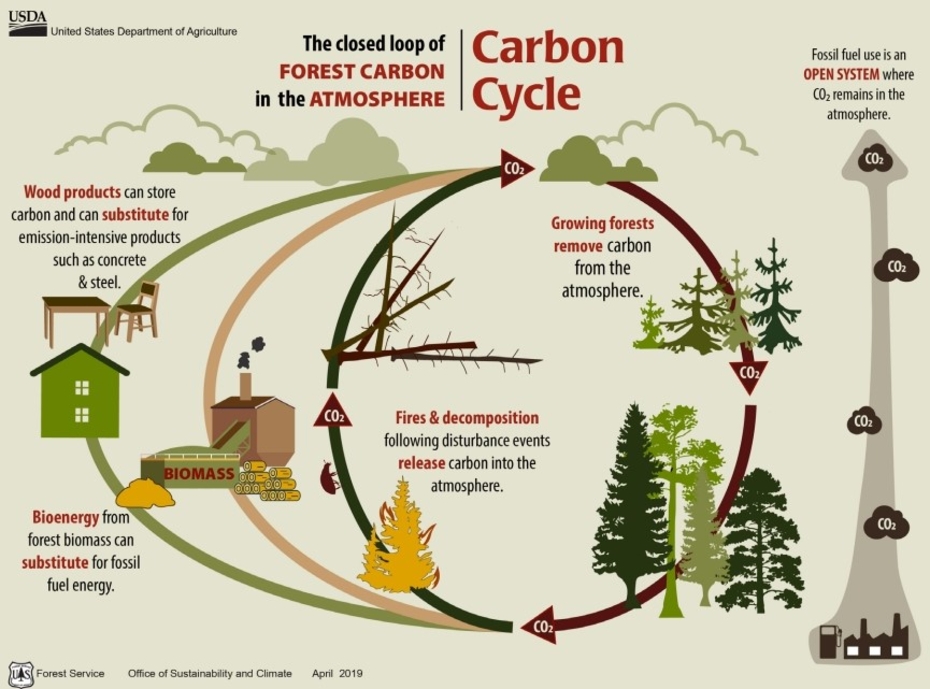
Forest carbon cycle with forest management. Source: USDA 2019.
This EU policy report explores how forest management can boost carbon sequestration. It analyses the potential of forest management practices as carbon farming measures and points out the challenges for monitoring and implementing mitigation milestones in carbon farming practices. The report also explores the policy and economic framework and recommends key criteria for the successful implementation of carbon farming instruments.
This report examines EU forest management practices that can potentially improve carbon sequestration in forest ecosystems. It analyses their potential as carbon farming measures and points out the challenges for monitoring and implementing mitigation milestones in carbon farming practices. The report also explores the policy and economic framework and recommends key criteria for the successful implementation of carbon farming instruments.
Carbon farming practices aim to enhance the carbon sequestration potential of forests and soils as well as avoiding or reducing greenhouse gas emissions. European multifunctional forest management aims to simultaneously enhance carbon removal and storage, as well as forest resilience and adaptation to climate change. Management practices such as afforestation (planting trees in an area with no recent tree cover), diversifying forest structure and composition, extending rotation periods or reducing harvesting intensity, site fertilisation as well as agroforestry or peatland management, can all contribute to reaching climate targets while maintaining forest multifunctionality and biodiversity. The EU has put in place a framework to implement carbon farming initiatives and is developing a regulatory framework for the accounting and certification of carbon removals from the atmosphere and wood products.
- Integrative Forest Management
- Funders & Investors
- Landowners & Practitioners
- Policy Actors
- 2024

