Forest and Soil Restoration Table
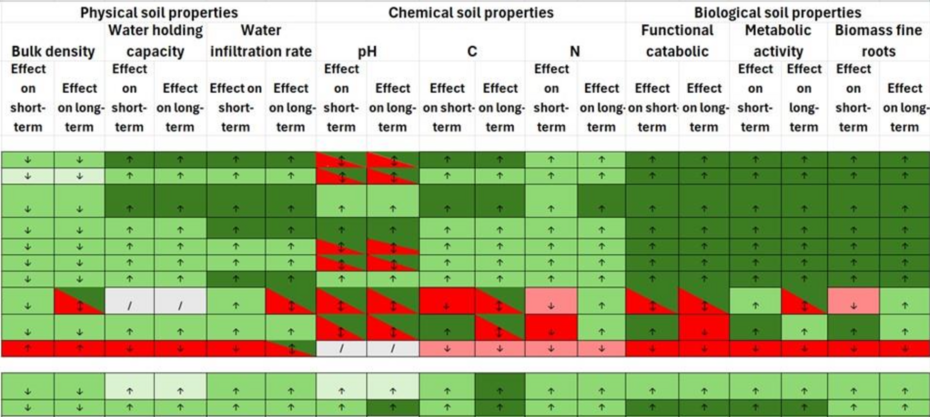
An Excel table containing forest restoration measures and their short- and long-term impact on different soil parameters.
An Excel table that outlines various forest restoration measures and their effects on key soil parameters. This table offers a practical overview for assessing the benefits and limitations of different approaches to forest and soil restoration. Colours indicate a positive or negative effect, while the arrows indicate if there is an increase or decrease of the soil properties. When interpreting this table, it is important to consider that factors like previous land use and implementation quality can strongly influence soil recovery outcomes.
This tool presents an overview of restoration guidelines containing restoration techniques and their short- and long-term influence on different aspects of soil health (proxied by the proposed scalable indicators). The effects of the different techniques are categorized using symbols (arrows), indicating if the soil parameter in question increases or decreases, and colors, indicating the intensity of the effect on the soil parameter. The tool serves as a practical reference for assessing the potential benefits and drawbacks of each approach in soil restoration and management.
When interpreting the table, several important disclaimers should be taken into account. First, previous land use plays a critical role in shaping the trajectory of soil recovery during restoration. Soil carbon, in particular, often reflects strong legacy effects from historical land use, which can persist for decades and influence the apparent success or failure of restoration interventions. Second, the way restoration measures are implemented significantly affects their impact. The quality and precision of management practices matter greatly. For example, when clearcutting is carried out using fixed skid trails, the extent of soil degradation is substantially reduced compared to more ad hoc approaches. Likewise, during soil preparation activities like ploughing, it is crucial to avoid excessive disturbance: ploughing too deeply can lead to long-term damage to soil structure and function. These nuances of implementation, which can determine the effectiveness of a restoration measure, are not captured in the table but are essential for accurate interpretation. Third, fire management practices such as controlled burning or the establishment of firebreaks can have localized negative effects on soil properties at the site of application. However, these interventions may provide important protective benefits at the landscape level by reducing the risk and severity of uncontrolled wildfires. As such, while their immediate impact on soil may appear detrimental, their broader role in preserving forest integrity must also be considered.
Finally, these guidelines represent an initial expert-based assessment of the potential effects of forest restoration measures on soil properties. They are mostly informed by interviews with specialists, our own fieldwork and a limited body of scientific literature. Due to limited availability of these peer-reviewed data, some evaluations remain qualitative or preliminary. As such, the guidelines should not be interpreted as definitive, but rather as a starting point for discussion and refinement.
Kind of License: Not stated/unknown
- Implementation
- Integrative Forest Management
- Monitoring & Projecting
- Landowners & Practitioners
- Planners & Implementers
- Policy Actors
- Soil health
- None/Non-relevant

