How to measure outcomes in forest restoration?
A European review of success and failure indicators
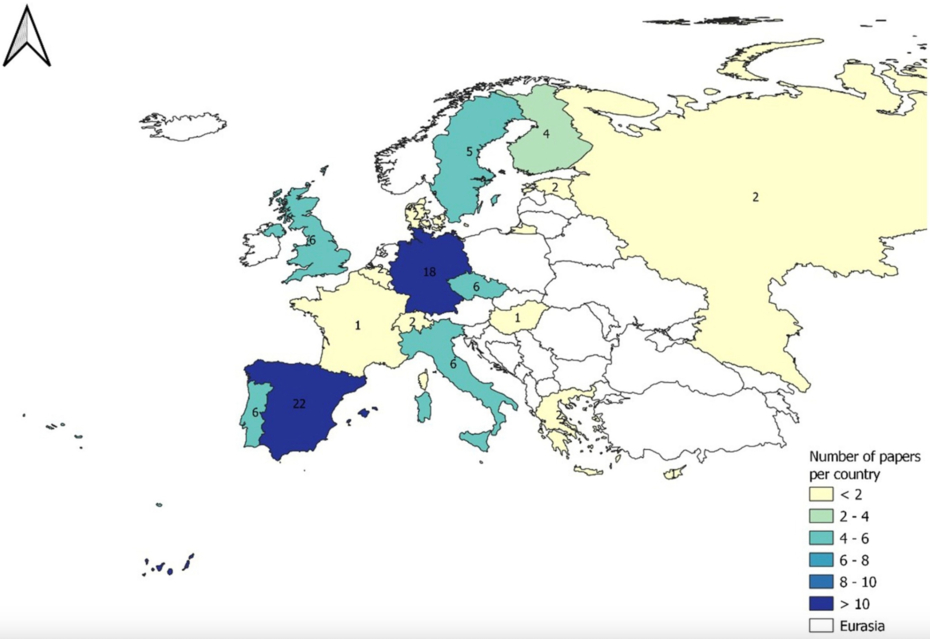
Reproduced from the original publication (Frontiers, 2024)
Scientific paper which analyzes 95 ecological restoration projects in Europe and identifies 84 indicators used to assess their success. It highlights five common metrics (abundance, cover, density, Ellenberg index, and richness) and emphasizes the need for harmonized indicators to evaluate restoration effectiveness, particularly under climate change. Useful for improving the planning and assessment of restoration initiatives.
Restoration involves the recovery and repair of environments because environmental damage is not always irreversible, and communities are not infinitely resilient to such harm. When restoration projects are applied to nature, either directly or indirectly, these may take the form of ecological, forestry, or hydrological restoration, for example. In the current scenario of global climate change and increasing intensity of disturbances, the importance of restoration in all types of ecosystems in order to adapt to the new conditions (so-called prestoration) is evident. Whatever the objective of the restoration initiative, there is a lack of consensus as regards common indicators to evaluate the success or failure of the different initiatives implemented. In this study, the authors carried out an extensive meta-analysis review of scientific papers aiming to evaluate the outcomes of restoration projects. They conducted a review and selected 95 studies implemented in Europe. The study explored the main pre-restoration land cover in which restoration initiatives have been implemented, the main causes of degradation, the objective of the restoration action, and the indicators selected to analyze the success or failure of the action. The researchers identified a total of 84 indicators in the analyzed papers and compared them with those proposed for forests in the recent Nature Restoration Law. The analysis revealed five indicators commonly used for the evaluation of restoration initiatives (abundance, coverage, density, Ellenberg indicator, and richness), even where the initial objective has not yet been achieved. The findings underscore both the benefits and challenges associated with a specific set of harmonized indicators for evaluating the success or failure of restoration initiatives.
- Active Restoration
- Monitoring & Projecting
- Passive Forest Restoration
- Landowners & Practitioners
- Planners & Implementers
- Policy Actors
- Afforestation, reforestation
- Non-timber products
- Restoration after direct human impact
- Restoration after natural disturbances
- Soil health
- Structural diversity
- Tree species/functional diversity
- Wood and biomass production
- Show 5 more
- Continental
- Mediterranean
- Austria
- Belgium
- Finland
- Germany
- Italy
- Portugal
- Russia
- Spain
- Switzerland
- United Kingdom
- Show 7 more
- 2024

