Restoration Practices Knowledge Base
1.4 Mulching

In the context of site preparation for tree planting, mulching involves applying a layer of organic or synthetic material to the soil surface around planting areas or seedlings. This technique is widely used to improve soil conditions, suppress weeds, retain soil moisture, prevent soil erosion, andmoderate soil temperature, all of which contribute to successful tree establishment and soil conservation. In general, the suppressive effect of the mulch bed is determined by its depth along the soil profile.
I. Guidelines
| Nº | Title | Author | Year | Focus Region | Language | Summary |
| 1 | Weed Control Methods Handbook; Chapter 1 – Manual & mechanical control techniques | Tu et al. | 2001 | World | English | Tools & Techniques to control invasive weed species in Natural Areas |
| 2 | The process of forest mulching: A step-by-step guide | Dreamworks Tree Services | 2024 | World | English | Guide for mulching |
II. Books or book chapters
| Nº | Title | Author | Chapter | Chapter author | Year | Focus region | Language | Summary |
| 1 | Ecological intensification of natural resources for sustainable agriculture | Kumar et al. | Mulching and weed management towards sustainability | Mechergui et al. | 2021 | World | English | Describes mulching as a means to improve site conditions, including weed control |
III. Scientific articles
| Nº | Title | Author | Year | Focus region | Language | Type | Summary |
| 1 | The assessment of mulch sheets to inhibit competitive vegetation in tree plantations in urban and natural environment | Samyn and De Vos | 2002 | Belgium | English | Experiment | Compares the cost and effect of mulch sheets vs traditional weed control (mowing, herbicides) on seedling performance |
| 2 | The Effect of Wood Mulch Type and Depth on Weed and Tree Growth and Certain Soil Parameters | Greenly and Rakow | 1995 | US | English | Experiment | Evaluates the effect of different mulch types and amounts on site conditions and seedling performance of Pinus strobus and Quercus palustris |
| 3 | A Comparison of Herbicide and Mulch Mat Treatments for Reducing Grass, Herb, and Shrub Competition in the BC Interior Douglas-Fir Zone—Ten-Year Results | Harper | 2005 | British Columbia | English | Experiment | 10-year experiment comparing the effects of several herbicide and mulch treatments on Douglas fir performance |
| 4 | Effect of Mulching on Plant and Weed Growth, Substrate Water Content, and Temperature in Container-grown Giant Arborvitae | Amoroso et al. | 2010 | Italy | English | Experiment | Evaluates the effects of biodegradable mulches for weed control on western redcedar and on soil evaporation and temperature |
| 5 | Mulching fuels treatments promote understory plant communities in three Colorado, USA, coniferous forest types | Fornwalt et al. | 2017 | US | English | Experiment | Investigates the ecological effects of mulching in the understory of stands of different tree species |
| 6 | Herbicides and forest vegetation management: A review of possible alternatives | Mc Carthy and Mc Carthy | 2005 | World | English | Conceptual review | Discusses alternatives to herbicide in weed control, including mulching |
| 7 | Impact of Mulches on Landscape Plants and the Environment — A Review | Chalker-Scott | 2007 | World | English | Narrative review | Compares the costs and benefits of landscaping mulches as reported in the scientific literature. |
| 8 | Influence of Mulches on Weed Control, Soil pH, Soil Nitrogen Content, and Growth of Ligustrum japonicum | Billeaud and Zajicek | 1989 | World | English | Experiment | Determine the influence of different mulch depths for weed control on soil pH, soil nitrogen and growth of Ligustrum japonicum |
Related resources
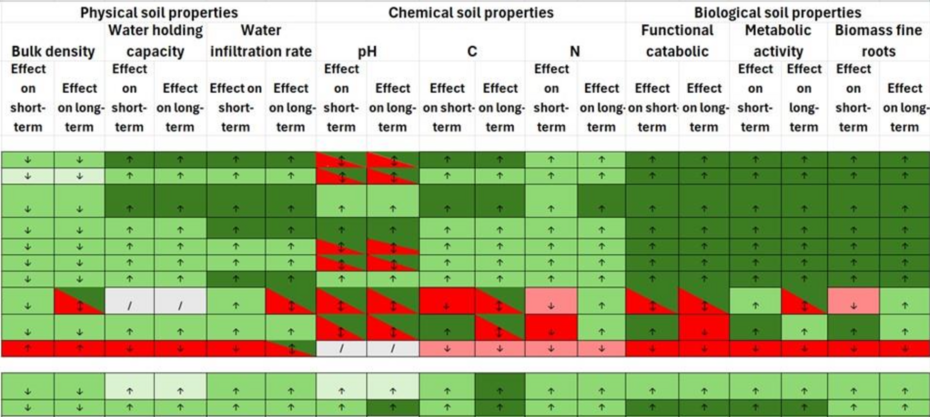
Forest and Soil Restoration Table
An Excel table that outlines various forest restoration measures and their effects on key soil parameters. This table offers a practical overview for assessing the benefits and limitations of different approaches to forest and soil restoration. Colours indicate a positive or negative effect, while the arrows indicate if there is an increase or decrease of the soil properties. When interpreting this table, it is important to consider that factors like previous land use and implementation quality can strongly influence soil recovery outcomes.