Restoration Practices Knowledge Base
5.5 Rockdust application

Rockdust application, also often called remineralization, involves amending soils with finely ground silicate rocks to replenish essential minerals and counteract soil acidification. This method enhances soil fertility by slowly releasing nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, and potassium, which are vital for plant growth and overall ecosystem health. The gradual weathering of rock dust improves nutrient availability and increases the soil buffer capacity, making it particularly beneficial for restoring degraded or acidified forest soils. Research in European contexts shows that rockdust application can improve soil nutrient status and support target vegetation development. Its effectiveness depends on factors like rock type, particle size, and site-specific soil properties, among others.
I. Scientific articles
| Nº | Title | Author | Year | Focus region | Language | Type | Summary | Link |
| 1 | Restoration rocks: The long-term impact of rock dust application on soil, tree foliar nutrition, tree radial growth, and understory biodiversity in Norway spruce forest stands | Van Der Bauwhede et al. | 2024 | Austria | English | Experiment | Long-term impacts and benefits of rock dust application in Norway spruce stands | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2024.122109 |
| 2 | The potential of rock dust nanoparticles to improve seed germination and seedling vigor of native species: A review | Arnott et al. | 2021 | World | English | Narrative review | Review on the use of rock dust as a soil amendment and its potential use of nanopriming | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.145139 |
| 3 | Soil pollution in Indian coal mines, available remediation techniques and rock dust application: A review | Chakraborty et al. | 2023 | India | English | Narrative review | Review focusing on how rock dust can be applied in soil remediation, looking into research gaps and conflicts | https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-023-02163-5 |
| 4 | Does rock dust work as a recovery measure against soil acidification in arid grasslands? | Bobbink et al. | 2020 | Netherlands | Dutch | Experiment | The study looks into the effectiveness of rockdust application against acidification in sandy arid grasslands | https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/20210341502 |
| 5 | Soil remineralization and recovery of degraded areas: An experience in the tropical region | Huff Theodoro et al. | 2021 | Brasil | English | Experiment | Experiment on degraded lands in the Brasilian Cerrado with a rock dust application method | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsames.2020.103014 |
| 6 | Plant growth and use of rockdust-amended compost in land restoration | Szmidt et al. | 2016 | UK | English | Experiment | Use of rockdust with and without compost as soil amendment for plant establishment at a landfill restoration project | https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2016.1146.25 |
Related resources
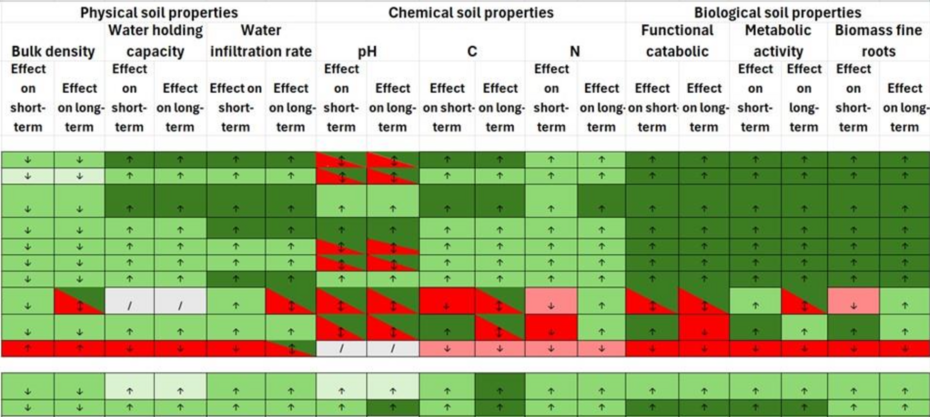
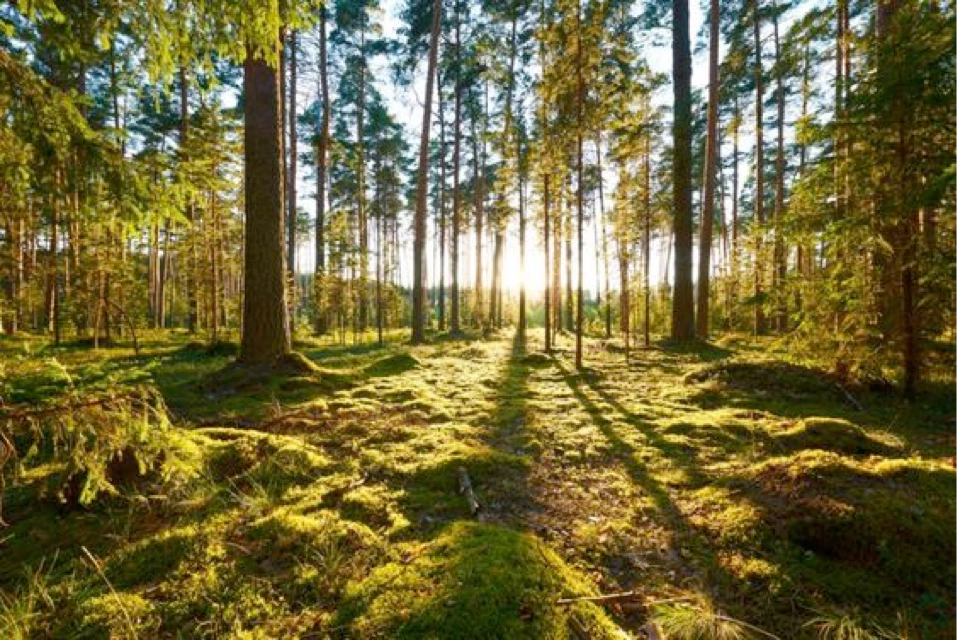
Forest and Soil Restoration Table
An Excel table that outlines various forest restoration measures and their effects on key soil parameters. This table offers a practical overview for assessing the benefits and limitations of different approaches to forest and soil restoration. Colours indicate a positive or negative effect, while the arrows indicate if there is an increase or decrease of the soil properties. When interpreting this table, it is important to consider that factors like previous land use and implementation quality can strongly influence soil recovery outcomes.
Soil Restoration and Monitoring Guidelines
Forests are essential ecosystems, covering approximately 35% of Europe’s land area. They harbour a significant share of Europe’s terrestrial biodiversity and provide a wide range of ecosystem services critical to European citizens. However, forests across Europe are increasingly threatened by various forms of degradation, driven by multiple, often anthropogenic factors.